We are all very aware of the term intrusion and have experienced it at one point or another in our lives. Rarely is an intrusion a good thing; its literal definition is an intentional attempt to enter someone else’s territory. Now, suppose you apply that to cyber security. In that case, the intrusion is when a malicious threat actor tries to get access to one’s system without their knowledge or approval. An Intrusion Detection and Prevention System (IDPS) is designed to identify these actions and prevent them from causing harm to your system. In the current world where businesses rely overtly on technology, IDPS has become a necessity to keep them safe. This blog will highlight various aspects of IDPS, including definitions of intrusion and detection, how this process works, types and benefits.
What Is Intrusion?
Intrusion, by definition, means getting into a territory unwelcome. So, what Is Intrusion in Cyber Security? Well, it is referred to as any illegitimate activity conducted on a network or a system. Network invasions almost always result in data security or network security breaches and frequently involve the theft of valuable network resources. There are many ways for hackers to commit intrusions. They may enter your network from the outside or from within (as an employee, client, or business associate). Hackers make use of tools and resources to infiltrate into their victim’svictim’s security. Some examples of intrusion include ransomware attacks, DDoS attacks, phishing campaigns, etc. Certain incursions are only attempts to alert you to their presence, while some are more malevolent.
What Is Intrusion Detection?
Intrusion detection, as the name suggests, refers to the ability to detect an intrusion. The main focus of intrusion detection is keeping an eye out for any malicious activities or network infractions. Usually, information regarding hostile activities or violations is gathered and disclosed when and how they are observed. Authorisation and identity play a significant role in intrusion detection. This implies that users must have valid identification and level clearance in order to access restricted locations or equipment. It is observed that laws and rules serve as a baseline for easy detection of an intrusion. Making sure there are no infractions is the responsibility of intrusion detection. Detection itself can be divided into several categories, one of which is physical intrusion detection. Organisations need to thoroughly understand how these attacks work to detect and respond proactively to network intrusions and implement intrusion detection and response systems designed explicitly with attack techniques and cover-up strategies in mind. Next, we explain what IDPS is.
What Is an Intrusion Detection & Prevention System?
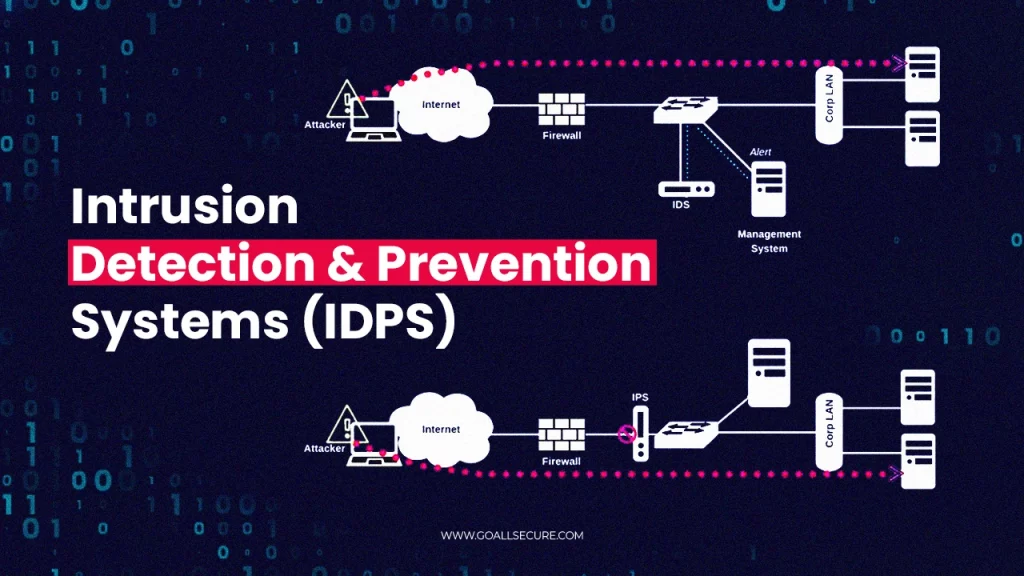
Network security defences heavily rely on intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS), which are frequently integrated to form intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS). They look through system logs for risks and assist in detecting, tracking, and blocking harmful software and traffic. Similar to how a home alarm system is intended to warn you of an attempted break-in, an intrusion detection and prevention system also monitors network traffic and alerts you to any unusual behaviour.
Now, one can employ various cyber security tools and resources to detect intrusions like firewalls and antivirus software. Still, they must not be confused with IDPS. A software program or hardware tool called an intrusion detection and prevention system keeps an eye out for hostile activity or network infractions. This system gathers and reports any risks or violations and reacts to discovered intrusions. Advanced IDPS mechanisms analyse the incident before taking the necessary action to eliminate the threat. These systems are more an evolved version of traditional security mechanisms and are a boon to business.
How Does an IDPS Work?
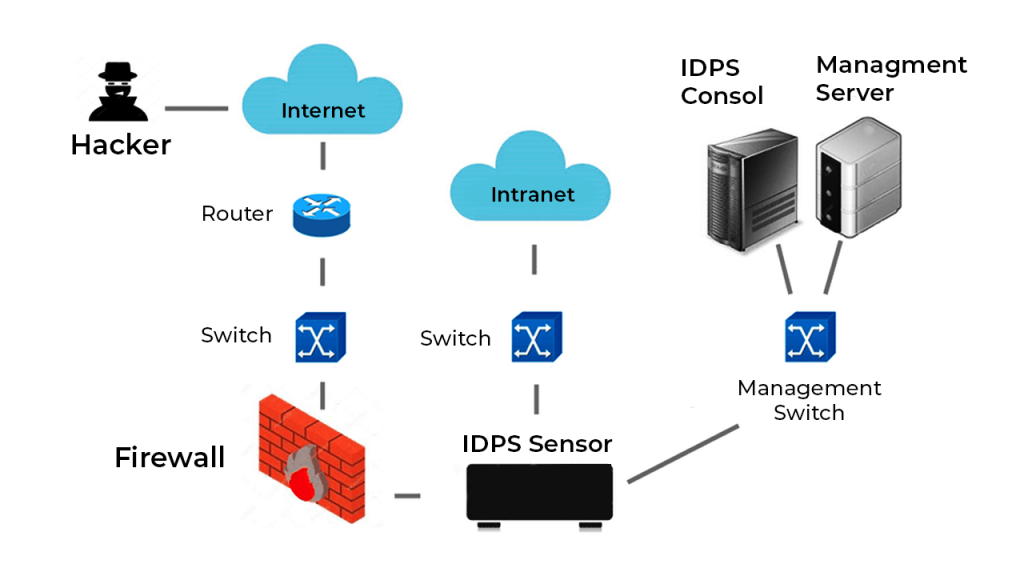
An IPS, like an IDS, scans network traffic for unusual activity and, like an IDS, intercepts threats in real-time by automatically cutting connections or initiating further security measures. In general, an IDS is passive. While it is unable to take action, it analyses network traffic and alerts an administrator to any potential hazards. Because an IPS can automatically respond to and rectify intrusions, it is a development of intrusion detection. An IDPS is a combination of both. IDPSs are typically installed inline, meaning all traffic must pass through the IPS before it can access the rest of the network because their primary purpose is to thwart cyber attacks. An incident response team is notified to look into a possible threat or policy violation by an intrusion detection system. IDPSs also track security occurrences; these logs can be used to update the network behaviour model or include new attack signatures, among other ways to improve the IDPS’s criteria.
An IDPS’s functionality consists of detection and prevention, as the name implies. To put it another way, it is the manner in which threats are detected and removed by the system. Potential occurrences are found by comparing signatures to recorded events using signature-based detection. This is the simplest detection method since it uses string comparison operations to compare only the current unit of activity (such as a packet or log entry) to a list of signatures. In protocol analysis, deviations are found by comparing observed events to preset profiles of commonly accepted standards for benign protocol activity for each protocol state. When the IDPS notices suspicious activity, it can initiate a variety of automated responses, such as resetting the connection, discarding packets, blocking traffic coming from the source address, and notifying administrators. In addition, many IDPS can actively stop a threat from being successful when recognised.
Types of Intrusion Detection Systems
IDPS systems were designed to do two primary tasks, i.e. intrusion detection and prevention. Now, there are various ways and parameters to be considered in doing the said tasks; depending on how the collected data is used in the end, IDPS may seem to behave slightly differently. Let’s look at various IDPS system types and their primary functions. Based on an organisation’s requirement, they can pick any one of the following IDPS.
Network-Based IDS
A network-based intrusion detection system monitors network traffic for individual network segments and analyses it to spot unusual activities. It can recognise a wide range of events and is typically installed at network boundaries, such as firewalls or remote access servers.
Host-Based IDS
A host-based intrusion detection system keeps an eye out for unusual activity by monitoring specific aspects of activities taking place on a host. This entails monitoring file access and modification, system and application configuration changes, running processes, network traffic, system logs, and application activity. The majority of the time, host-based IDSs are installed on vital hosts, such as public servers.
Wireless IDS
In order to spot suspicious activities, a wireless intrusion detection system keeps an eye on wireless network traffic and examines protocols. It is unable to detect unusual activity in higher-layer network protocols or applications. Although it can also keep an eye out for unauthorised wireless networking, it is most frequently placed within the scope of an organisation’s wireless network.
Network Behavior Analysis (NBA) System
An NBA system scans network traffic to find threats such as distributed denial of service (DDoS) assaults, specific types of malware, and policy breaches that cause anomalous traffic flows. NBA systems can also track traffic leaving an organisation by monitoring flows on its internal networks, which is where they are most frequently utilised.
Benefits of Using an IDPS
There is a reason why IDPS is popular and has had a substantial place in cyber security. Despite numerous modifications and groundbreaking breakthroughs throughout the course of their decades-long existence, intrusion detection prevention systems continue to be an essential component of practical cyber defence. They are usually installed in front of firewalls to act as an extra layer of defence against malicious activity. Some pivotal benefits of IDPS include:
- Increased attack visibility leads to increased protection for business and less danger.
- Enhanced efficiency makes inspecting all traffic for risks possible, leading to more security.
- Reduced resource requirements for patching and vulnerability management as IDPS lessens the effort and boosts the effectiveness of other security controls by screening out hostile traffic before it reaches them.
- An IDPS saves a lot of time as it requires less effort from IT teams because it is mainly automated.
- An IPS meets many of the PCI DSS, HIPAA, and other regulatory compliance criteria.
- An IDPS can be configured with customised security policies to offer security controls unique to the business using it.
- Before any serious harm is done, IDPS may identify any unusual activity and notify the system administrator.
Features to Consider Before Choosing the Best IDPS for Your Business
The terms intrusion prevention system (IPS) and intrusion detection system (IDS) are used interchangeably. With one crucial exception, the functions of an IDS and an IPS are almost identical: an IPS sends an alert and takes proactive measures to address suspicious activity, whereas an IDS only sends a warning if a danger is discovered. When combined, they create an IDPS that can enhance your business’s security manifold. Here are some features that you should look for while choosing an IDPS for your business:
- Efficiently track the functionality of the security and IT hardware.
- Prompt in identifying and reporting data file tampering detected by the IDS.
- Provides admins a means of adjusting, arranging, and comprehending important OS audit trails and additional logs that are otherwise challenging to follow or interpret.
- Possess an extensive attack database that can be used to compare system data.
- Offers a user-friendly interface so that staff members without technical expertise may help manage system security
- Quickly alert the user to a security breach and take action against hackers by blocking the offending user or server.
- Most importantly, the IDPS that you choose must fit your budget.
Best Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems In 2024
When we take into account the startling 150% increase in DDoS attacks in the first half of 2024, IDPS suddenly becomes more useful. Intrusion prevention systems can analyse and react to all network traffic flows automatically because of their inline deployment. The best IDS systems help provide security at deeper layers of the network. We have compiled a list of intrusion detection and prevention systems for you. Among the products on this list are some of the best open-source IDS as well.
- Check Point Quantum IPS
- Cisco Secure IPS
- Snort
- Trend Micro TippingPoint
- Security Onion
- SolarWinds
- BluVector Cortex
- Suricata
- OSSEC
- Zscaler Cloud IPS
- Fidelis Network by Fidelis Security
- Trellix Intrusion Prevention System
- Hillstone S-Series Intrusion Prevention System
- NSFOCUS
- OpenWIPS-NG
- Secureworks Managed iSensor Network Intrusion Prevention System
- McAfee Network Security Platform
- AIDE (Advanced Intrusion Detection Environment)
- Palo Alto Networks Threat Prevention
- SecBlade IPS
How GoAllSecure Can Help?
The traditional intrusion detection technologies that are typically employed could be better. Old and rusty detection techniques, poor database management, and some other difficulties encountered in conventional IDPS can call for the use of next-generation technology. GoAllSecure offers thorough and complete real-time network protection against a wide range of network threats. We conduct extensive exercises to detect and prevent any threats heading towards your network. We can assist you in minimising false positives, or false alarms, to a zero. With our team, you will get swift deployment of IDPS products, ensuring their correct installation so that they can distinguish between potentially malicious activities and regular network traffic. If you have more queries regarding intrusion detection systems, get in touch with us right now!
FAQs:
Q: Which Is the Most Effective Type of Intrusion Detection System?
A: The effectiveness of an IDS depends on your requirements. However, the most used types of intrusion detection systems are signature-based and network-based, which detect both known and unknown malicious activities.
Q: Does a Firewall Contain an IDS or IPS?
A: Yes. IDS and IPS features are present in genuine next-generation firewalls. However, not every firewall is a next-generation firewall, so not all firewalls have an IPS or IDS.
Q: Can an IDPS Help Identify Insider Threats?
A: Yes, an IDPS can help identify insider threats because it searches for unforeseen modifications like deletion, overwriting, and access to specific ports, which is very effective against insider threats. System administrators receive alerts for questionable activity.
Q: Are IDS and IPS the Same?
A: No, IDS and IPS are different systems. The former is focused on detecting intrusions, while the latter works on prevention. When combined, they create IDPS, an intrusion detection and prevention system.
Q: Where Is IDPS Installed?
A: The placement of IDPS in your network infrastructure depends on its type. The IPS is positioned inline, between the source and the destination, right in the middle of the network traffic flow. The IDS location, however, needs to be out of band or beyond a direct line of communication.
Q: What Benefits Does an IPS System Offer?
A: A threat detection system (IPS) can help you detect malicious activities, record and report threats, and take proactive measures to stop threats before they do significant harm.
Q: Is a DDoS Attack Preventable by an IPS?
A: An IPS can stop certain kinds of DDoS attacks. Its functionality can detect and defend against very basic threat types. Nonetheless, a specific solution is needed for volumetric DDoS attacks.















 TRAVEL & HOSPITALITY
TRAVEL & HOSPITALITY HEALTHCARE
HEALTHCARE RETAILS & ECOMMERCE
RETAILS & ECOMMERCE BANKING & FINANCIAL
BANKING & FINANCIAL AutoMobile
AutoMobile MANUFACTURING
MANUFACTURING FOOD
FOOD EDUCATION
EDUCATION