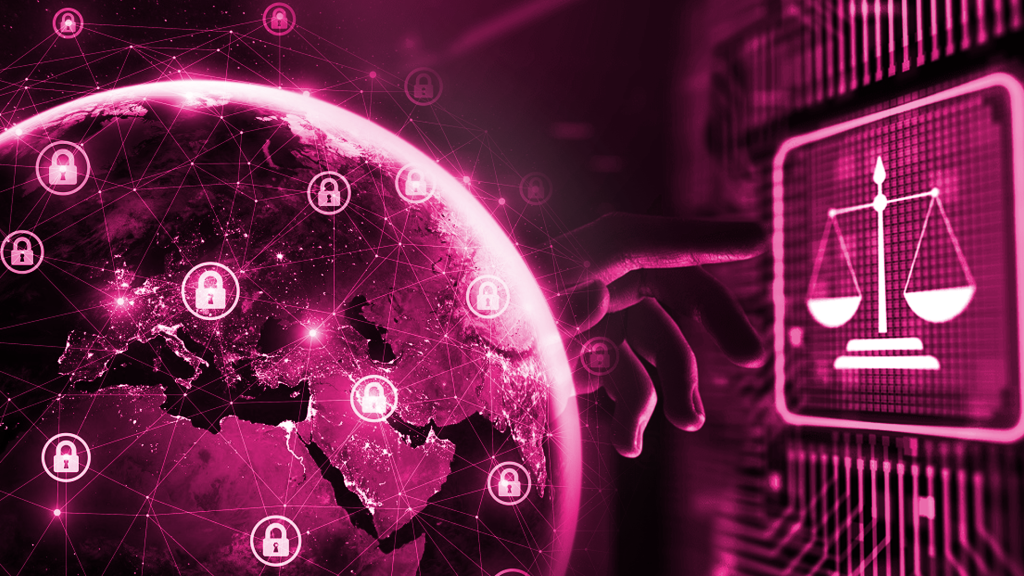
Cyber security has been elevated to a top priority for all countries in today’s interconnected world. Strong international Cyber security rules are more important than ever because of the frequency and sophistication of cyber threats. The current state of international Cyber security regulations, however, is fraught with difficulties. This blog examines the characteristics of international Cyber security legislation, identifies problem areas, and makes recommendations for future changes to create a more efficient and comprehensive framework for global cyber security legislation.
What Are Cyber Laws?
The division of the legal system that deals with legal information and regulates e-commerce, software, and information security is known as cyber law, also referred to as Internet law or cyber law. It is connected to electronic components like computers, software, hardware, and information systems, as well as legal informatics. It covers a wide range of issues, including online privacy and freedom of expression, as well as how to access and use the Internet.
Cyber law focuses on the legal ramifications of computing, the internet, and cyber space. It has under its jurisdiction a wider range of topics, including those related to intellectual property, contracts, jurisdiction, data protection regulations, privacy, and freedom of expression in the digital sphere.
How Can Cyber Laws Protect Us?
Using the Internet poses many security risks, and numerous malevolent individuals attempt to get unauthorised access to your computer system to commit potential fraud. As with any law, cyber law was developed to safeguard online businesses and network users from harmful actors and unauthorised access. It allows people or organisations the opportunity to have that person sentenced to punishment or take action against them if they engage in any criminal behaviour or violate the cyber regulation.
Cyber law provides a range of legal safeguards for Internet users and those operating online businesses. Here is what cyber laws are needed for:
- To act as a buffer between internet users and online data predators.
- To guarantee victims of cyber crimes receive justice.
- To make sure that the private and sensitive data of individuals as well as organisations is secure. Knowing about cyber law makes it simple to take preemptive action.
- To avoid online payment gateways and credit card or debit card theft, as the majority of people now use digital payment methods.
- To secure the safety of a nation by keeping its governmental data protected.
What Is the State of Current Cyber Laws?
Cyber space is not specifically governed by international law. For a long time, it was unclear whether or not Cyber space was covered by existing international law. Today, most states have their own regulations for cyber crimes and none of them see eye to eye with one another. As a result, cyber crimes have been affecting both buyers and sellers across the world and are an increasing worry for nations at all stages of development.
Here is a list of major cyber security regulations that are globally acknowledged:
- Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) – United States (1986)
- Data Protection Directive (95/46/EC) – European Union (1995)
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
- Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) – United States (1999)
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) – United States (2002)
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) – European Union (2018)
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) – United States (2020)
- Network and Information Security Directive (NIS Directive) – European Union (2016)
- Cyber security Law – China (2017)
Security of any kind needs the support of legislation to uphold the peace. The same is true with cyber security; it needs unified legislation that is capable enough to put the miscreants behind bars and restore harmony and calm. Global law and regulation to defend the victims of cyber fraud and punish the offenders is a big priority for achieving equilibrium in international cyber space. The current state of cyber laws looks something like this:
- 156 nations (80%) have laws against cyber crime in place; however, the implementation rates vary by region, with Europe having the highest adoption rate at 91% and Africa having the lowest adoption rate at 72%.
- 80% of the countries in the world have legislation, while 5% of the countries have draught legislation. There are a whopping 13% of the countries that have yet to have any legislation at all for cyber crimes.
- Cyber laws encompass areas like e-transactions, consumer protection, data protection/privacy and cyber crime. Every country has adopted laws for either all or some of them. Today, 81% of countries have e-transactions laws, and 59% of countries have solid consumer protection laws. There are 71% of countries with privacy laws in place, while 80% have specific cyber crime laws.
What Is the Problem with Existing Laws?
The lack of effective international legal rules in cyber space has mostly been a delight for the malicious threat actors and a great deal of unnecessary botheration to the victims and internet users. This issue needs to be explored in theoretical as well as policy-making debates.
It is not a new idea to consider using international law to govern cyber space. Since 1996, nations, commercial entities, and legal experts have all suggested (and denied) several draughts of an international cyber space law. Some of the fundamental challenges in international cyber law are:
- Complexities of Jurisdiction: Cyber space knows no physical boundaries, making it challenging to attribute cyber attacks to specific individuals or nations. This creates difficulties in enforcing laws and prosecuting cyber criminals, as traditional legal systems often struggle to adapt to the transnational nature of cyber threats.
- Diverse Legal Frameworks: Each country has its own set of Cyber security laws, regulations, and standards, resulting in a fragmented global landscape. This disparity hampers international cooperation, information sharing, and coordinated responses to cyber incidents.
- Lack of Consensus: The absence of a unified understanding and consensus on key Cyber security concepts and norms poses a significant challenge. Different countries may have differing interpretations of cyber threats, offensive capabilities, and acceptable behaviour in Cyber space, making it difficult to establish common ground.
- Rapid Technological Advancements: Cyber threats evolve rapidly, outpacing the development of legislation. Emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and the Internet of Things, introduce new vulnerabilities and complexities that traditional laws struggle to address effectively.
Since it is difficult for nation-state actors to reach an agreement regarding cyber space, creating an agreeable and enforceable law seems like a problem that could never be solved!
What Are the Solutions that We Need?
The current state of international cyber security laws faces several challenges, ranging from jurisdictional complexities to diverging legal frameworks. To improve global cyber space, all the international players need to come together and join hands to defend against the common enemy. Here are a few things that can help accomplish the idea of a protected cyber space:
- Enhanced collaboration and information sharing among nations, industry stakeholders, and international organisations. Establishing dedicated channels for timely and secure information sharing to facilitate proactive responses to cyber incidents.
- Encourage nations to align their cyber security laws and regulations with international standards and best practices. This would enable smoother cooperation, streamline legal processes, and enhance cross-border investigations and prosecutions.
- Establishing and encouraging the development of internationally accepted norms and principles for responsible state behaviour in cyber space. This would help build consensus on acceptable conduct, discourage malicious activities, and provide a foundation for stronger international cyber security cooperation.
- Encourage countries to review and update their cyber security laws regularly to keep pace with evolving threats and technological advancements.
The question of a unified international cyber law may be a distant dream, but your organisation’s current security status does not need to be. Cyber security specialists at GoAllSecure are working to keep ahead of notorious threat actors and keep the online world well-protected. We are well prepared to protect you and your business from cyber attacks. We have a bona fide offensive approach to identifying threats and vulnerabilities to defend you. For more information about us, kindly visit us at https://www.goallsecure.com/ or call us at +91 85 2723 7851 or +44 20 3290 4885.















 TRAVEL & HOSPITALITY
TRAVEL & HOSPITALITY HEALTHCARE
HEALTHCARE RETAILS & ECOMMERCE
RETAILS & ECOMMERCE BANKING & FINANCIAL
BANKING & FINANCIAL AutoMobile
AutoMobile MANUFACTURING
MANUFACTURING FOOD
FOOD EDUCATION
EDUCATION



